
What is Lipodystrophy?
Lipodystrophies are a group of rare conditions that affect very few people. They are characterised by a lack of subcutaneous fat (fat under the skin) with this being the main sign of the condition.
Generalised lipodystrophy
The whole body is affected by the lack of fat.
Partial lipodystrophy
Certain areas of the body is affected by the lack of fat.
Subcutaneous fat is part of the body‘s adipose tissue.
Patients with lipodystrophy have less fat – isn’t that a good thing?
If you have too little subcutaneous body fat, it can make you very ill. We need a certain amount of body fat. Why? Because our fat has important functions which allow us to lead healthy lives with an even distribution of fat throughout the body.
Lipodystrophy is characterised by partial or complete absence of adipose tissue. There are four main subtypes – congenital generalised lipodystrophy, acquired generalised lipodystrophy, acquired partial lipodystrophy and familial partial lipodystrophy.
Fact: Lipodystrophies are always linked to a lack of subcutaneous fat. But the extent and location of fat loss depends on the form of lipodystrophy.
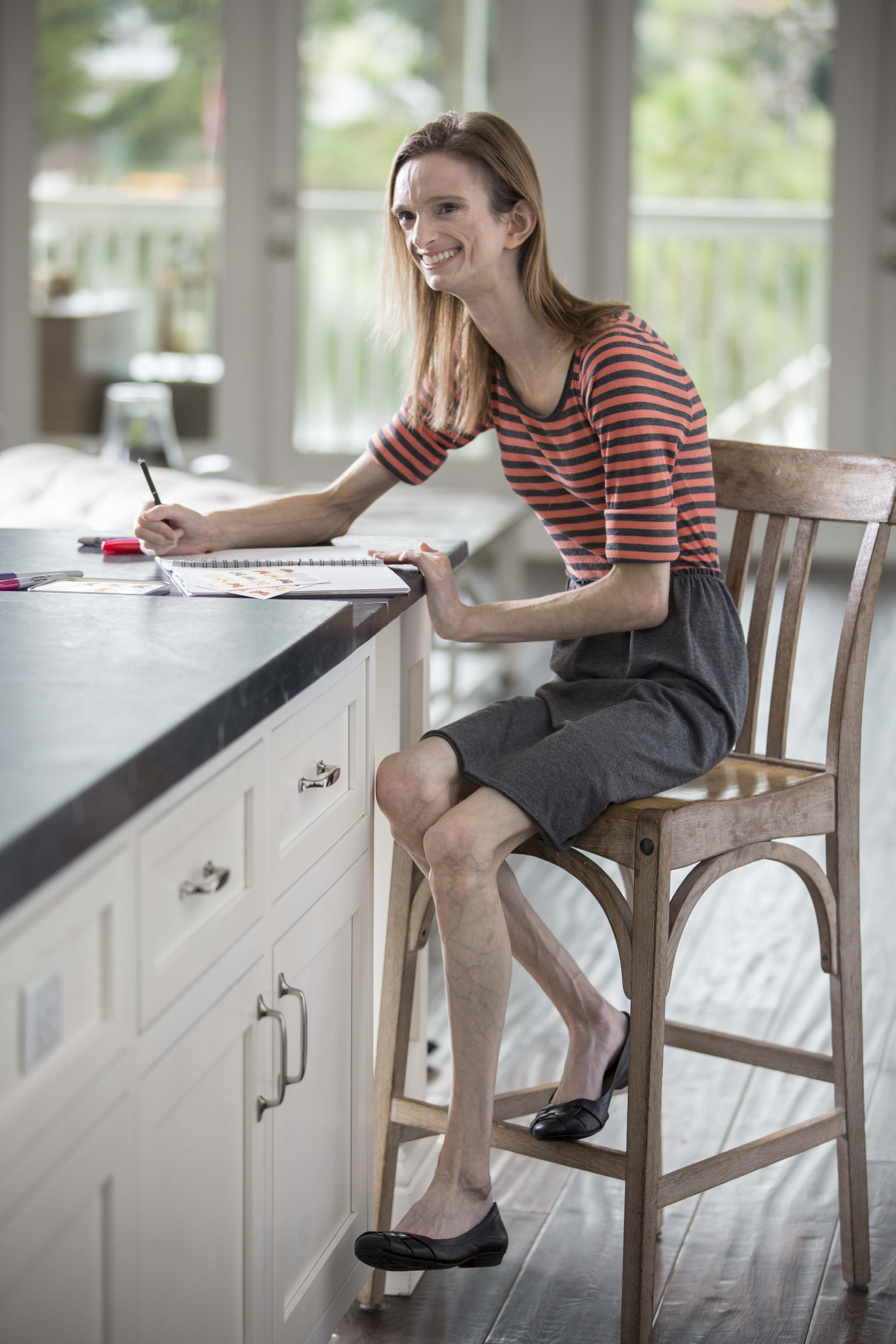

What is the Adipose Tissue for?
Adipose tissue is normally found in many parts of the body, including beneath the skin and surrounding the internal organs. It stores fat as a source of energy and also provides cushioning.
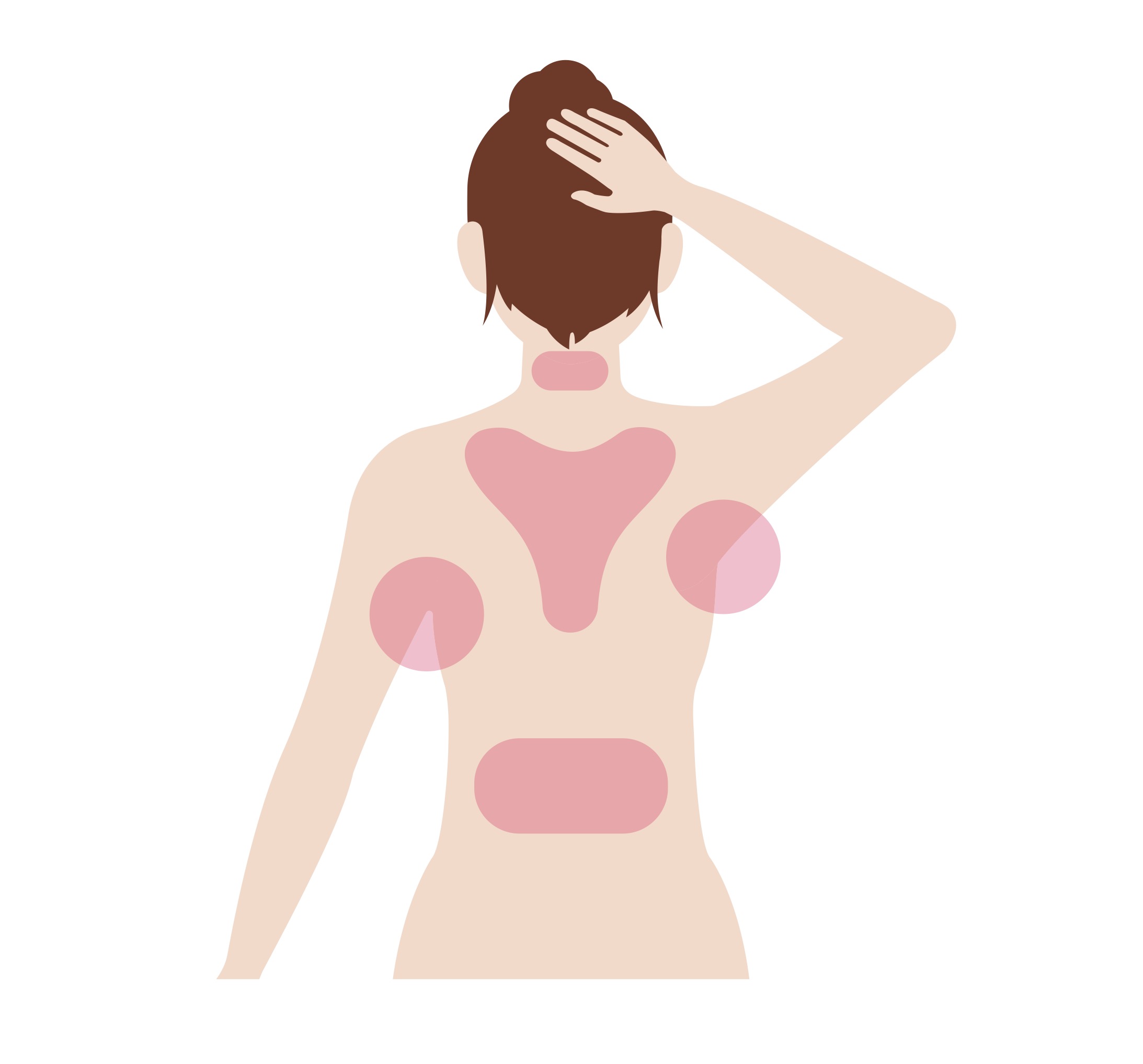
In losing fat under the skin, lipodystrophy patients have lost much of their energy storage capacity and once the remaining capacity is exceeded, excess energy is stored in other organs such as liver, spleen and muscles. In people with familial partial lipodystrophy for instance, adipose tissue is lost from the arms, legs, and hips giving these parts of the body a very muscular appearance.
The fat that cannot be stored in the limbs builds up where subcutaneous fat remains such as in the neck and face. This abnormal fat distribution can begin anytime from childhood to adulthood.
The role of the hormone Leptin
If you have too little subcutaneous body fat, it can make you very ill. We need a certain amount of body fat. Why? Because our fat has important functions which allow us to lead healthy lives with an even distribution of fat throughout the body.
Lipodystrophy is characterised by partial or complete absence of adipose tissue. There are four main subtypes – congenital generalised lipodystrophy, acquired generalised lipodystrophy, acquired partial lipodystrophy and familial partial lipodystrophy.
